How to choose the right generator

Power outages can happen anytime — and when they do, having a generator can make all the difference. Whether you need backup power for your home, a reliable source for your job site, or energy independence in off-grid locations, generators are an essential tool for keeping things running smoothly.
In this guide, we’ll explore the different types of generators, their most common uses, and what to consider when choosing the best generator for your needs.
What Is a Generator?
A generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Most generators are powered by gasoline, diesel, propane, or natural gas, while others run on solar energy or are connected to wind turbines.
When the main power supply fails — whether due to weather, technical faults, or planned outages — generators step in to provide electricity for essential appliances, tools, or systems.
Common Uses for Generators
Generators are used across various settings, from residential backup power to powering remote worksites and supporting large-scale events.
In homes:
Generators provide emergency backup power to keep lights on, refrigerators running, and medical equipment functioning during blackouts. Many homeowners invest in portable or standby generators for peace of mind.
On job sites:
Construction crews rely on portable generators to power tools and lighting in areas where electrical hookups are unavailable.
In businesses:
Generators are crucial for data centers, hospitals, and restaurants to avoid service disruptions and financial losses during power outages.
In off-grid or recreational use:
Campers, RV owners, and off-grid homes use generators as a primary power source, especially where grid power is unavailable or unreliable.
Types of Generators
There are several types of generators, each suited to specific needs and environments. Here’s a breakdown of the most common options:
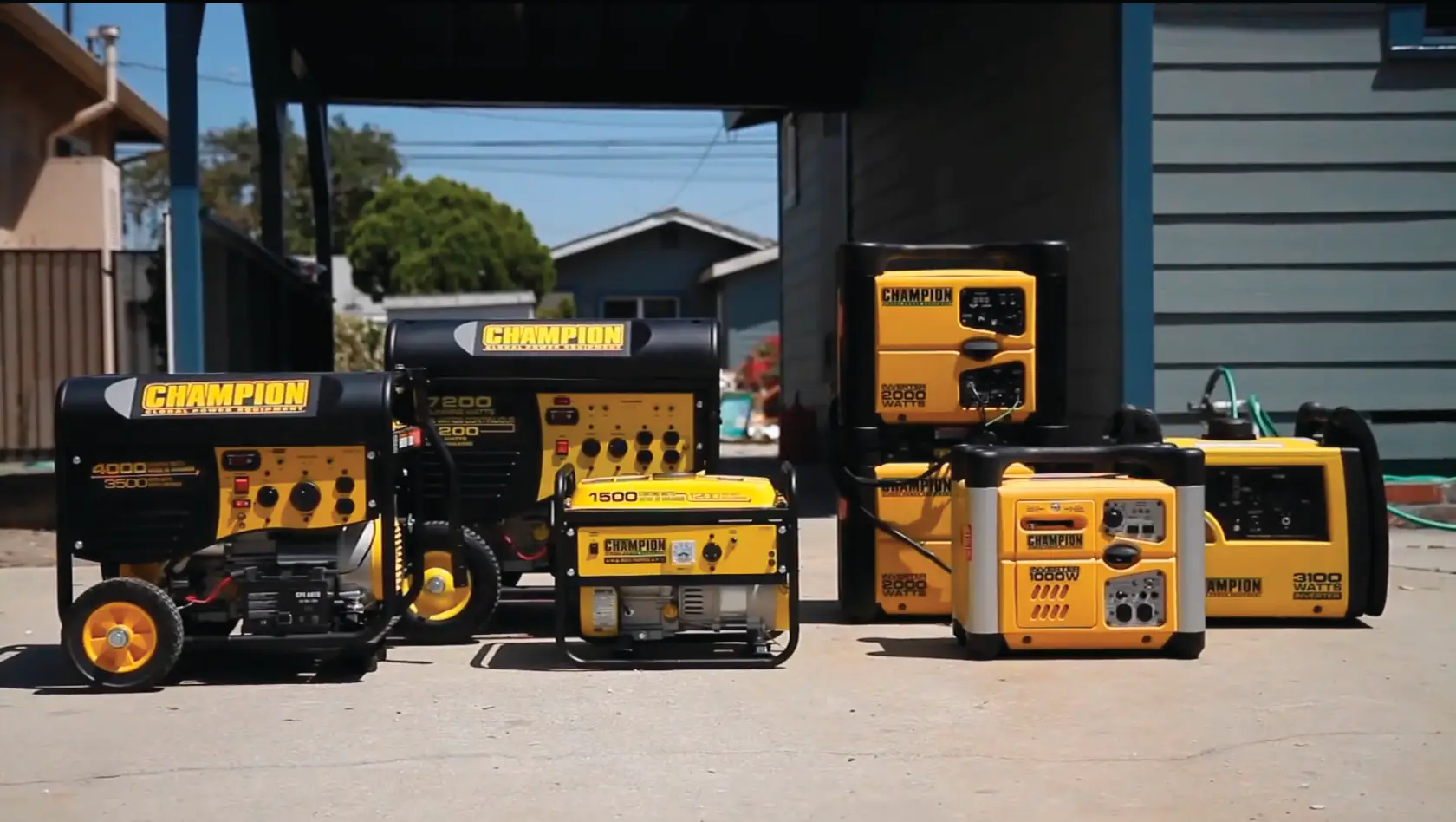
Portable Generators
These are compact, mobile units that run on gasoline or diesel and are ideal for short-term, light-duty use. Perfect for home emergencies, camping trips, or small job sites, portable generators can power lights, appliances, and tools.
Inverter Generators
Known for being quiet and fuel-efficient, inverter generators provide clean, stable power that’s safe for sensitive electronics like laptops, TVs, and mobile devices. They’re often used for camping, tailgating, and light home use.
Standby Generators
Also called backup generators, these are permanently installed outside a home or business and connected to the building’s electrical system. They automatically kick in when the main power fails. These units typically run on natural gas or propane and can power an entire home or facility.
Industrial Generators
Designed for large-scale operations, industrial generators are built to handle heavy electrical loads and extended use. They’re common in factories, hospitals, data centers, and remote industrial sites.
Solar Generators
These eco-friendly generators use solar panels to charge internal batteries. While not suitable for heavy loads, they’re a great choice for small electronics, outdoor events, or emergency kits.
How to Choose the Right Generator
Choosing the right generator comes down to a few essential factors:
1. Power Requirements
Start by calculating your total wattage needs. List the devices or appliances you want to power and add up their wattage. This will help you choose a generator with enough starting (surge) and running watts.
For example:
- A fridge: ~700 watts
- A microwave: ~1,000 watts
- Lights, chargers, fan: ~500 watts combined
A 3,000-watt generator would comfortably handle this setup.
2. Fuel Type
Generators typically run on:
- Gasoline – widely available, but not ideal for long-term storage
- Diesel – efficient and durable, often used in industrial models
- Propane – cleaner-burning and storable long-term
- Natural gas – used in standby generators, piped directly from your utility supply
- Solar – ideal for lightweight, eco-conscious power needs
Choose based on fuel availability, cost, and environmental preference.
3. Portability vs. Permanence
If you need a temporary or mobile power solution, a portable or inverter generator is ideal. For consistent, automatic backup power at home or work, a standby generator is the better long-term investment.
4. Noise Level
Generators can be loud, especially gas-powered models. If you’re using one in a residential neighborhood or during camping, look for quiet or inverter generators that produce less noise (typically under 60 dB).
5. Runtime and Efficiency
Check the runtime (how long the generator can run on a full tank or charge) and fuel efficiency, especially if you’ll be using it for extended periods.
6. Safety Features
Look for built-in safety options like:
- Low oil shut-off
- Overload protection
- Carbon monoxide detectors
These features help prevent damage to the generator and protect your household or crew.
Maintenance Tips
To keep your generator running reliably:
- Run it every few months to prevent engine issues
- Check oil and air filters regularly
- Store fuel properly and stabilize it if needed
- Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule
Regular upkeep ensures your generator will be ready when you need it most.
Investing in the right generator gives you the power to stay connected, productive, and safe — no matter the situation. From weekend camping trips to critical backup power during emergencies, there’s a generator out there to meet every need.
Take the time to assess your power requirements, environment, and budget before choosing. With the right unit and proper maintenance, a generator can serve you well for years to come.